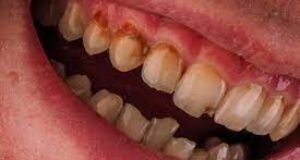
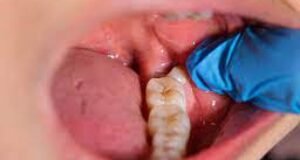
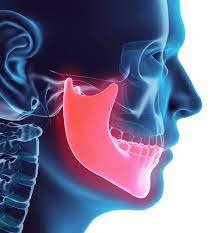
A Tooth Abscess or a Dental Abscess is a mouth, face, throat, or jaw infection that originates as a tooth or cavity infection. If tooth decay is left untreated, it can reach the dental pulp. The nerve and blood vessels located at the center of the tooth become infected and die. The bacteria then spread beyond the end of the tooth, soon creating an abscess. The primary reason for this is improper dental care. Essentially, the bacteria from the cavity spread to the gums, beneath the tongue, cheek, facial bones, jaw, or throat. The tissues may become inflamed. In the area of infection, pus can develop, causing pain until it drains automatically or through surgery. Swelling can occur to a point where breathing is hampered. This kind of abscess can be accompanied by chills, nausea, sweats, and fever. Additionally, wisdom tooth causing jaw pain is another common dental issue, often leading to discomfort and potential complications if not addressed properly.
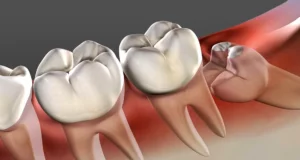
Types of Tooth Infection
A “Periapical abscess” usually comes from the dental pulp and is widespread in children. A “Periodontal abscess” starts in the supporting bone and tissue structures of the teeth and is commonly seen in adults.
Causes of Tooth Infection
If an individual does not properly brush and floss regularly, cavities are likely to form inside the teeth. The bacteria present in these cavities move towards the soft tissues and bones of the face and neck. Eventually, the tooth infection spreads to the gums and adjacent areas, forming a painful dental abscess. Sugar present in the diet turns into acid, which attacks tooth structures. Similarly, impacted wisdom teeth can create pressure and lead to jaw pain, making it crucial to maintain proper oral hygiene and consult a dentist if discomfort arises.
Symptoms of Dental Infection
- Redness of the mouth and face, swelling, and pain
- Nausea, vomiting, chills, fever, diarrhea
- Inflammation of the gum
- Tenderness upon touch
- Drainage of pus
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- Presence of cavities
- Raised tooth
- Presence of raised bumps in areas like the armpits, groin, and neck
- Sensitivity to heated liquids or foods
- Jaw pain caused by wisdom tooth impaction
Diagnosis
If local pain worsens when pressing or chewing with the affected tooth, a possible dental abscess can be assumed. X-rays are useful in detecting small dental abscesses in the deepest portion of the tooth. A dentist will perform a physical examination to determine if the abscess is drainable. If symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills occur, it indicates that the infection has spread to the extent that the entire body is affected. Wisdom tooth-related jaw pain can also be diagnosed through X-rays, revealing whether extraction is necessary.
Treatment of Tooth Infection
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen help alleviate pain and inflammation. If the abscess breaks on its own, warm water rinsing can cleanse the mouth and facilitate drainage. The natural burst of an abscess is termed a gum boil. To prevent the reappearance of the abscess, a root filling should be placed inside the tooth, a procedure known as “endodontics” or “root canal treatment.” With the use of a normal filling or crown, the tooth can be restored. If the abscess does not rupture naturally, a dentist may cut it open to allow the pus to drain. Pain relievers and antibiotics may be prescribed to fight the infection. If the infection spreads to the lower mouth or neck, anesthesia can be administered for pus drainage. In the case of wisdom tooth causing jaw pain, extraction may be necessary if the tooth is impacted or causing severe discomfort.
Prevention
- Brushing and flossing with fluoride toothpaste after every meal and at bedtime
- Cleaning between teeth using dental floss or interdental brushes
- Reducing the frequency of sugary food intake
- Detecting and treating cavities at an early stage
- Avoiding cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption
- Regular dental check-ups to monitor wisdom teeth and prevent potential jaw pain issues
By maintaining proper oral hygiene and seeking timely dental intervention, individuals can prevent abscess formation and avoid wisdom tooth-related jaw pain.